This collaborative project started in 2021 between the AUCTUS team at Inria, the RoBioSS team at the Pprime Institute (CNRS), and the Interaction team at the CeRCA laboratory (CNRS). It is co-funded by the ASAP-HRC young-researcher ANR grant and the Perception-HRI Nouvelle-Aquitaine Regional Aid. It aims at rethinking Autonomy for Shared Action and Perception in Human-Robot Collaboration, through transverse studies in robotics and cognitive sciences.
Three scientific axes are studied to develop a human-centered and generic shared-autonomy framework:
[Read More]
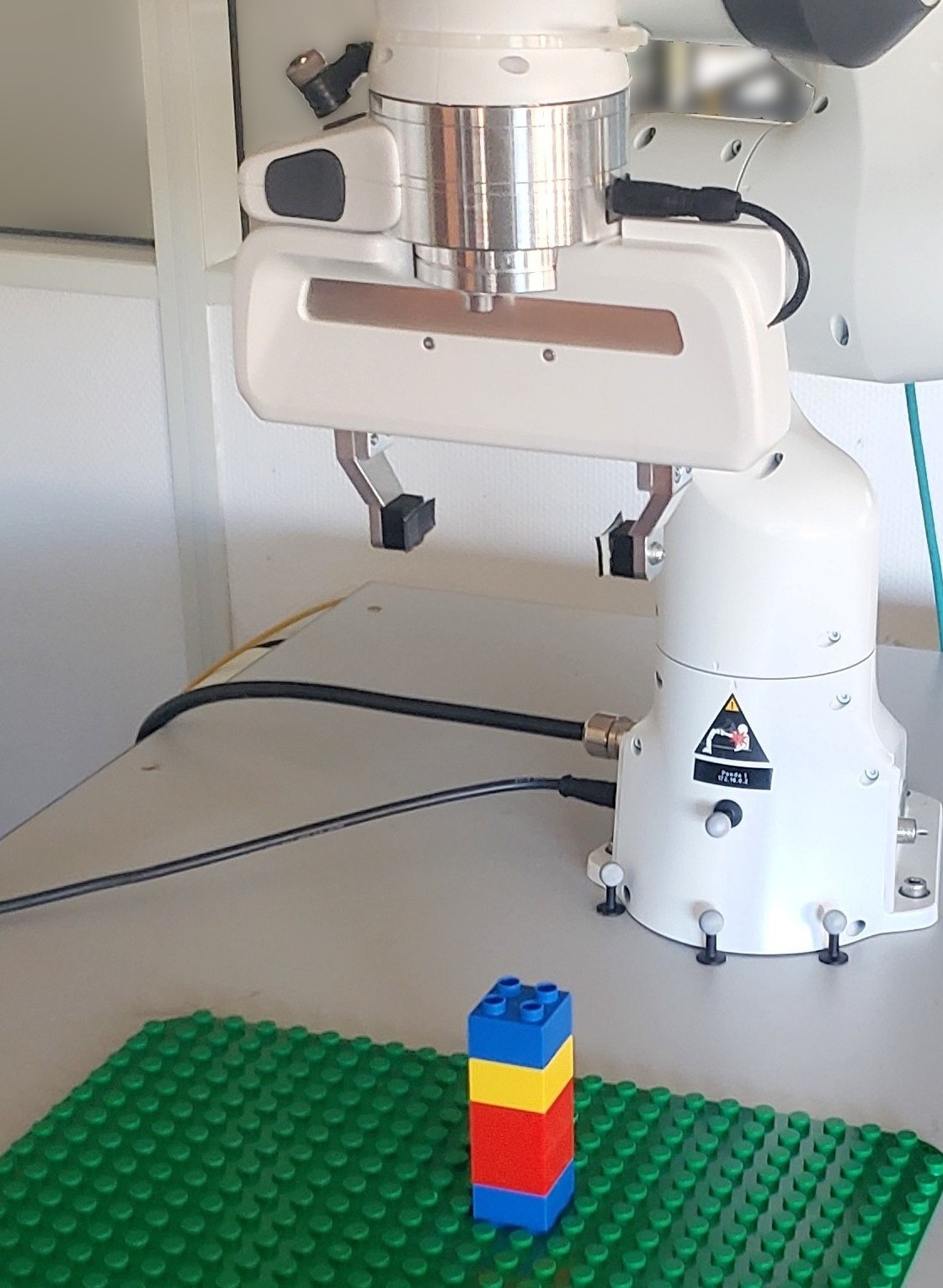
The aim of this project is to use pieces of softwares developed at Auctus to manipulate LEGO. This work can be related to experiments for Benjamin Camblor’s thesis and the PacBot project.
Live demonstration Here is a video of a manipulation demo. The robot realizes three tasks:
Remove a single LEGO on a tower Put LEGO on the plate Put LEGO on another LEGO All this work is done using the softwares developed at Auctus, namely :
[Read More]
The PacBot project aims to design a semi-autonomous cobotic system for assistance, capable of selecting, synchronising and coordinating tasks distributed between the human and the robot by adapting to different types of variability in professional gestures, while anticipating dangerous situations.
The orchestration of tasks between the human and the robot is difficult because it must answer the question of the distribution of roles within the couple according to the physical and decision-making abilities and constraints as well as the consequences of their interactions.
[Read More]
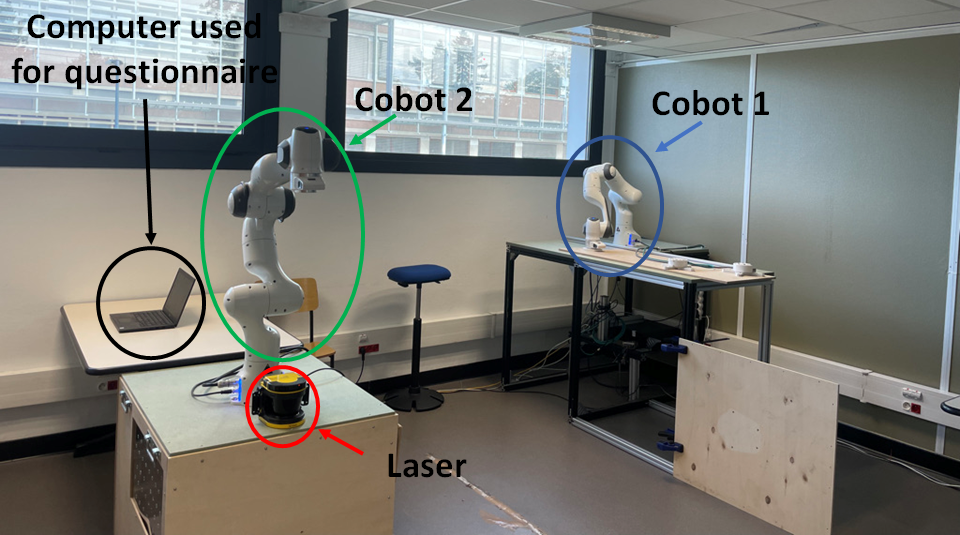
Paper Abstract In this paper, the concept of signaling motions of a robot interacting with a human is presented. These motions consist in using the redundant degrees of freedom of a robot performing a task as new means of meaningful robot-human communication. They are generated through quasi-static torque control, in consistency with the main robot task. A double within-subject (N=16) study is conducted to evaluate the effects of two signaling motions on the performance of a task by participants and on their behavior towards the robot.
[Read More]
PhD title: Shared Situational Awareness for task planning between a human and a robot
[Read More]